
Shell Commands
느낌표(exclamation mark)로 시작되는 코드 셀 내의 라인은 셀 커맨드로 실행된다. 이는 데이터셋을 비롯한 파일을 다룰 때나 파이썬 패키지를 관리할 때 유용하다. 간단한 예를 보자.
!echo Hello World!!Hello World!!pip freeze | grep pandaspandas==0.25.1
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.그리고 $ 심볼을 활용하여 파이썬 변수로도 활용가능하다.
message = 'This is nitfy'
!echo $messageThis is nitfy
Basic Magics
유닉스 명령어와 상당 부분 유사해보이지만, 매직 명령어는 모두 파이썬으로 구현된다. 크게 2개의 카테고리로 나누어지는데, line magics 과 cell magics 이 그것이다. 명칭 그대로 차이점은 싱글 라인에 작동하느냐, 아니면 멀티플 라인이나 전체 셀에 작동하느냐 여부다. 전체 매직 명령어를 다 보고 싶다면 아래와 같이 하면 된다. Line magics 은 % 로 시작하고, cell magics 은 %% 로 시작된다.
%lsmagic Available line magics:
%alias %alias_magic %autoawait %autocall %automagic %autosave %bookmark %cat %cd %clear %colors %conda %config %connect_info %cp %debug %dhist %dirs %doctest_mode %ed %edit %env %gui %hist %history %killbgscripts %ldir %less %lf %lk %ll %load %load_ext %loadpy %logoff %logon %logstart %logstate %logstop %ls %lsmagic %lx %macro %magic %man %matplotlib %mkdir %more %mv %notebook %page %pastebin %pdb %pdef %pdoc %pfile %pinfo %pinfo2 %pip %popd %pprint %precision %prun %psearch %psource %pushd %pwd %pycat %pylab %qtconsole %quickref %recall %rehashx %reload_ext %rep %rerun %reset %reset_selective %rm %rmdir %run %save %sc %set_env %store %sx %system %tb %time %timeit %unalias %unload_ext %who %who_ls %whos %xdel %xmode
Available cell magics:
%%! %%HTML %%SVG %%bash %%capture %%debug %%file %%html %%javascript %%js %%latex %%markdown %%perl %%prun %%pypy %%python %%python2 %%python3 %%ruby %%script %%sh %%svg %%sx %%system %%time %%timeit %%writefile
Automagic is ON, % prefix IS NOT needed for line magics.
Autosaving
체크포인트 파일에 자동 저장하는 주기를 %autosave 매직을 통해 셋팅할 수 있다.
%autosave 60Autosaving every 60 seconds
Displaying Matplotlib Plots
무엇보다도 데이터 과학자들이 가장 많이 사용하는 라인 매직은 %matplotlib 이다. 이를 통해서 노트북 자체에서 이미지나 챠트를 보여줄 수 있다. 실행 예제는 하단을 참고한다.
%matplotlib inline아나콘다에 matplotlib 라이브러리를 설치하는 방법은 다음 포스팅을 참고한다.
2018/12/15 - [리눅스 Linux] - 아나콘다 matplotlib 설치
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
plt.title("Plot")
plt.plot([1, 4, 9, 16])
plt.show()
Timing Execution
서로 다른 접근 방식을 런타임 차원에서 비교해야할 경우가 있다. IPython은 이와 관련하여 %time 과 %timeit 이라는 2개의 시간관련 매직을 제공한다. %timeit 이 %time 과 구분되는 점은, 특정 코드를 여러번 실행해서 그 평균값을 보여준다는 것이다. -n 옵션을 통해 반복횟수를 지정할 수도 있다.
n = 1000000
%time
total = 0
for i in range(n):
total += iCPU times: user 3 µs, sys: 0 ns, total: 3 µs
Wall time: 5.96 µs%timeit sum(range(n))17 ms ± 43.1 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
Executing Different Languages
앞서 살펴본 매직 명령어에 대한 섹션에서 %lsmagic 명령을 통해 다양한 매직명령어의 종류를 살펴볼 수 있었다. 특히 그 중에서 %perl %html %python 과 같은 프로그래밍 이름이 붙는 명령어를 볼 수 있었다. 이 명령어를 통해 특정 셀을 특정 언어로 실행이 가능하다. 다음은 HTML 을 렌더링하는 예제이다.
%%HTML This is <em>really</em> neat!UsageError: %%HTML is a cell magic, but the cell body is empty.
위의 UsageError 이 발생하는 경우, 라인을 바꿔서 다음과 같이 실행해주세요.
%%HTML
This is <em>really</em> neat!This is really neat!
마찬가지로 수학식을 표현해주는 LaTeX 라는 마크업 언어를 이용하여, 다음과 같은 표현도 가능하다.
%%latex
Some important equations:$E = mc^2$ $e^{i pi} = -1$
Configuring Logging
주피터에는 에러 및 경고 메시지를 보여주는 내장된 기능이 있다. 이해를 돕기 위해 실제 노트북 화면에서는 어떻게 나오는지 아래 예제를 통해 살펴보자. 로그 결과는 셀 아웃풋과는 또 다르게 표시되는데, 여타 셀 아웃풋보다 상단에 위치한다. 아래 그림을 보자.
import logging
print('Something printed')
logging.error('An Error')
logging.warning('A Warning')
'Some output'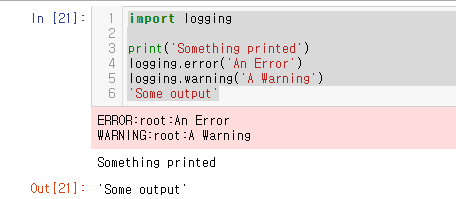
이것이 가능한 이유는 주피터 노트북은 standard output streams, stdout 와 stderr 을 listen하지만, 각각을 서로 다르게 취급하기 때문이다. stderr 을 통해 로깅을 다른 종류의 메시지를 표현하는데도 사용할 수 있다.
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
logging.info('This is some information')
logging.debug('This is a bug message')INFO:root:This is some information
DEBUG:root:This is a bug message그리고 아래와 같이 커스토마이징도 가능하다.
handler = logging.StreamHandler()
handler.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(Levelname)s: %(message)s')
logging.handlers = [handler]
logging.error('An Error')
logging.warning('An Error')
logging.info('An Error')ERROR:root:An Error
WARNING:root:An Error
INFO:root:An ErrorStreamHandler 대신에 FileHandler 를 사용하여 외부 파일에 로그를 남길수도 있다.
handler = logging.FileHandler(filename='important_log.log', mode='a')
원문보기 https://www.dataquest.io/blog/advanced-jupyter-notebooks-tutorial/
Advanced Jupyter Notebook Tutorial – Dataquest
If you're doing data science in Python, notebooks are a powerful tool. This free Jupyter Notebooks tutorial has will help you get the best out of Jupyter.
www.dataquest.io
'Season 1 아카이브 > 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Plotly를 이용한 데이터 시각화 Data visualization with Plotly (0) | 2019.10.26 |
|---|---|
| tqdm 을 사용하여 파이썬/판다 Progress Bars 만들기 (0) | 2019.10.24 |
| 아파치 웹서버 버추얼 호스팅 설정 How To Set Up Virtual Hosts in the Apache Web Server on Ubuntu 18.04 (0) | 2019.10.21 |
| 아파치 삭제 후 재설치 apache2.service is not active, cannot reload. (1) | 2019.10.18 |
| 커스텀 ML 툴을 만들어주는 가장 빠른 방법 Streamlit 앱 소개 Turn Python Scripts into Beautiful ML Tools (1) | 2019.10.12 |